Riccia – Morphology, Anatomy and Reproduction
Riccia is a simple thalloid liverwort belonging to Division Bryophyta. It is commonly studied to understand the basic structure and reproduction of liverworts. This blog post is about Riccia – Morphology, Anatomy & Reproduction Guide, You can download this note as PDF. Link provided at the end of the post. Happy learning…
Botany Notes | Botany PPTs | Botany MCQs
1. Morphology of the Gametophyte Thallus
External Features (Dorsal and Ventral View)
- The plant body is a flat, ribbon-like thallus that grows prostrate on moist soil.
- The thallus shows clear dorsiventral differentiation.
- Repeated dichotomous branching produces a rosette-like arrangement.
- Each branch is linear to wedge-shaped with a notch at the apex.
- A thick midrib runs along the center; a shallow groove is visible on the dorsal side.
- The ventral surface bears rhizoids and scales.
- Scales occur near the margins and appear violet in color.
- Rhizoids arise from the midrib region.

Rhizoids
Two types are present:
- Smooth-walled rhizoids – inner walls are smooth.
- Tuberculate rhizoids – inner walls form peg-like projections extending into the lumen.
Scales
- Violet colored
- Multicellular
- One cell thick
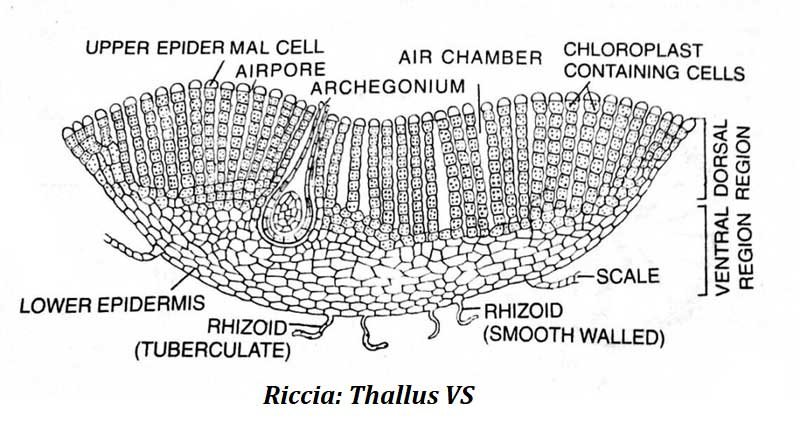
Sex Organs
- Embedded in the mid-dorsal groove.
- Mature sporophytes appear as black dots under a dissecting microscope.
| You may also like NOTES in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| BOTANY | BIOCHEMISTRY | MOL. BIOLOGY |
| ZOOLOGY | MICROBIOLOGY | BIOSTATISTICS |
| ECOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | BIOTECHNOLOGY |
| GENETICS | EMBRYOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY |
| EVOLUTION | BIOPHYSICS | BIOINFORMATICS |
2. Anatomy of the Riccia Thallus (Gametophyte)
A transverse section (T.S.) shows the internal organization.
General Structure
- The thallus appears boat-shaped in cross-section.
- It is thickest at the midrib and thinner at the edges.
- Two distinct regions are visible:
- Upper photosynthetic region
- Lower storage region
Storage Region
- Composed of compact parenchyma cells.
- Cells store starch.
- Bounded below by a lower epidermis.
- Rhizoids originate from this region.
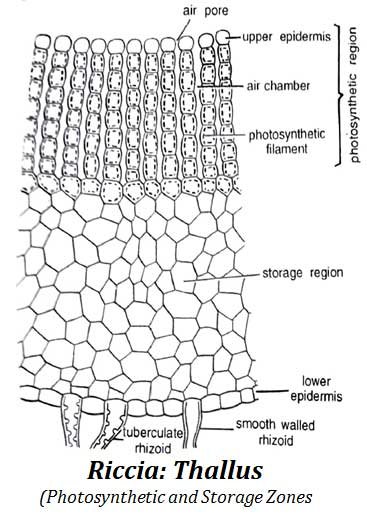
Photosynthetic Region
- Made of vertical, unbranched assimilatory filaments.
- Filaments are separated by narrow air chambers.
- Cells are barrel-shaped and contain many chloroplasts.
- Air chambers open outside through simple air pores.
- The uppermost cells lack chloroplasts and form an indistinct epidermis.
- Violet scales are visible near the margins in cross-section.
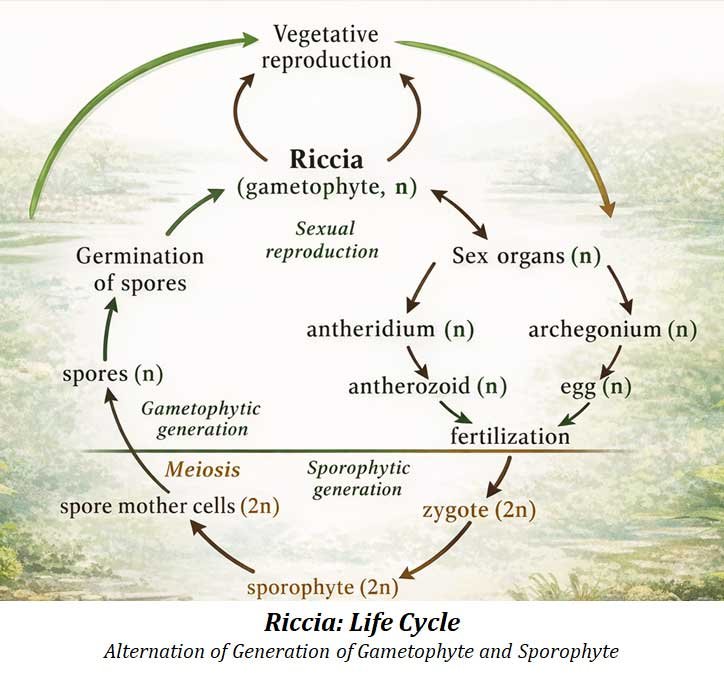
3. Riccia Antheridium (Male Reproductive Organ)
Key Features
- The plant is monoecious; both sex organs occur on the same thallus.
- Antheridia develop in the mid-dorsal groove.
- Each antheridium lies inside an antheridial chamber.
- The chamber opens to the exterior through a pore.
- The structure is partly embedded in both photosynthetic and storage regions.
Structure of Mature Antheridium
- Short multicellular stalk
- Globular or club-shaped body
- Central mass of androcytes (antherozoids)
- Surrounded by a single sterile jacket layer
- Jacket cells are tangentially elongated
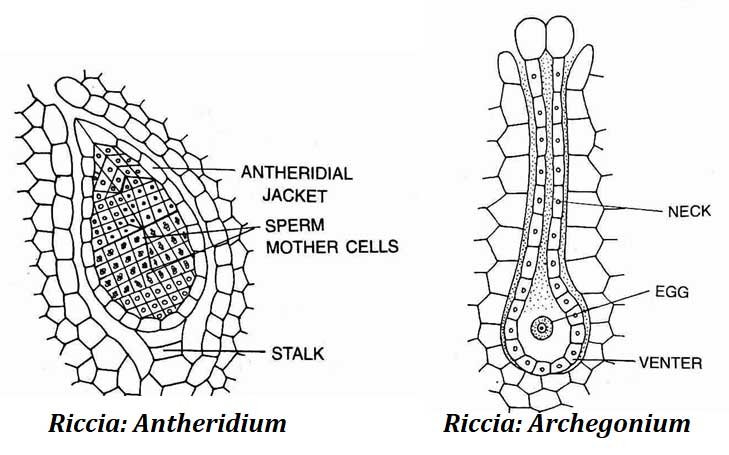
4. Riccia Archegonium (Female Reproductive Organ)
Key Features
- Located in the mid-dorsal groove.
- Flask-shaped at maturity.
- Short stalk present.
Structure
- Broad basal venter
- Long neck
Venter contains:
- One egg cell
- One venter canal cell
Neck contains:
- Six vertical rows of cells
- 6–9 cells in height
- Four neck canal cells
- Four cover cells at the tip
Before Fertilization
- All axial cells except the egg disintegrate.
- Cover cells separate.
- Passage is created for antherozoids to enter.
5. Riccia Sporophyte (Sporogonium)
General Characteristics
- Develops inside the fertilized archegonium.
- Remains embedded in the gametophyte tissue.
- Consists only of a capsule.
- Foot and seta are absent.
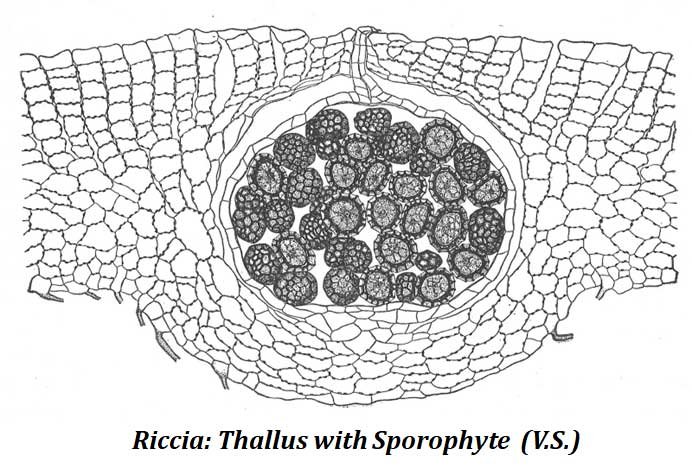
Capsule Development
- Young capsule has:
- A jacket layer
- Two-layered calyptra
- At maturity:
- Jacket and inner calyptra layer disintegrate
- Only outer calyptra remains
- Spores are released after the thallus decays.
Spores
- Arranged in tetrahedral tetrads initially.
- Each spore measures about 0.05–0.12 mm in diameter.
- Contains dense cytoplasm and a nucleus.
Spore Wall Layers:
- Exosporium – thin and cutinized
- Mesosporium – thick
- Endosporium – thin and homogeneous
- The wall surface is irregular and folded.
6. Systematic Position of Riccia
Division: Bryophyta
- True roots absent
- Vascular tissues absent
Class: Hepaticopsida
- Mostly thalloid forms
- Rhizoids non-septate
- Chloroplasts lack pyrenoids
- Capsule lacks columella
Order: Marchantiales
- Scales present
- Two types of rhizoids
- Air chambers and pores present
Family: Ricciaceae
- Simple air pores
- Sex organs in mid-dorsal groove
- Sporophyte reduced to capsule only
Genus: Riccia
- Scales at margins
- Assimilatory filaments vertical and unbranched
7. Habitat and Collection
- Common in both plains and hilly regions.
- Grows on damp soil and rocks.
- Often appears after heavy rainfall.
- Frequently found in unused soil or brick crevices.
8. Riccia fluitans (Aquatic Species)
- Only free-floating aquatic species of the genus.
- Thallus highly dichotomously branched.
- Ribbon-like, elongated and thin.
- Rhizoids and scales absent.
- Reproduces vegetatively through adventitious branches.
- Remains sterile while floating.
- Produces sex organs when water levels drop and it becomes terrestrial.

| You may also like... | ||
|---|---|---|
| NOTES | QUESTION BANK | COMPETITIVE EXAMS. |
| PPTs | UNIVERSITY EXAMS | DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. |
| MCQs | PLUS ONE BIOLOGY | NEWS & JOBS |
| MOCK TESTS | PLUS TWO BIOLOGY | PRACTICAL |
