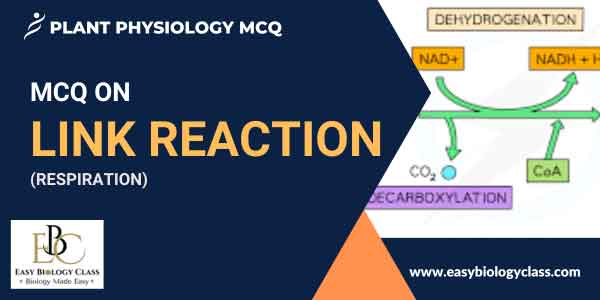
The link reaction, or pyruvate decarboxylation, is the process where pyruvate from glycolysis is converted into acetyl-CoA in the mitochondria. Pyruvate loses a carbon dioxide molecule, and NAD+ is reduced to NADH. This reaction connects glycolysis to the Krebs cycle. This is an MCQ on Link Reaction of Respiration or Pyruvate Decarboxylation Reaction in the cells.
<<< Back to Plant Physiology MCQ Page
You may also like... NOTES QUESTION BANK COMPETITIVE EXAMS. PPTs UNIVERSITY EXAMS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. MCQs PLUS ONE BIOLOGY NEWS & JOBS MOCK TESTS PLUS TWO BIOLOGY PRACTICAL