Stem: Stem is the part of the plant which lies above the surface of the soil. It arises from the plumule of the embryo. Stem shows positively phototropic and negatively geotropic growth. Stem possess nodes and internodes. Branches, leaf, flower bud and bracts are developed from nodes.
Root: Root is the part of the plant which lies below the surface of the soil. It arises from the radical of the embryo. Root shows positively geotropic and negatively phototropic growth. Root is not differentiated into nodes and internodes.
The present post summarize the anatomical difference between the Stem and Root with a Comparison Table.
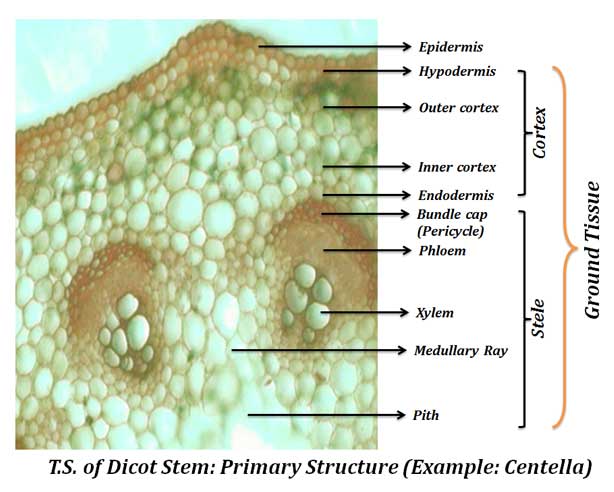
Difference between Root and Sstem Anatomy
Sl. No. Anatomy of Stem (Shoot) Anatomy of Root 1 Epidermal cells are cutinized in stem. Root epidermal cells are not cutinized. 2 Function of the epidermis is protection. Function of epidermis is absorption of water and nutrients. 3 Stomata are present in the epidermis of young stem. Stomata are completely absent. 4 Stem hairs unicellular or multicellular. Root hairs are always unicellular. 5 Stem hairs are NOT the out-growth of epidermis. Root hairs are the out-growth of epidermis 6 Cortex usually narrow. Cortex is broad 7 Hypodermis present Hypodermis usually absent. 8 Cortex usually differentiated into outer, middle and inner cortex. Cortex usually undifferentiated. 9 Outer cortical cells possess chloroenchyma. Chlorenchyma completely absent in roots. (Present in aerial roots). 10 Endodermis NOT distinct Endodermis distinct and prominent 11 Casparian thickening not prominent. Casparian thickening very prominent in the endodermis 12 Pericycle, if present, multilayered Pericycle is usually single layered. 13 Pericycle do not have any role in secondary thickening Pericycle has a role in secondary thickening. Lateral roots arise from endodermis. 14 Vascular tissue conjoint and collateral or bicollateral Vascular tissue radial. 15 Xylem endarch (protoxylem oriented towards the interior) Xylem exarch (protoxylem oriented towards the exterior) 16 Xylem and phloem contain fibres Fibres absent in the xylem and phloem


