Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are essential nucleic acids in biological systems, performing critical roles in the storage, transmission, and execution of genetic information. DNA is primarily responsible for the long-term storage of genetic information and is the blueprint for all biological functions. RNA, on the other hand, acts as a messenger and plays various roles in the expression of genetic information. This article discusses the similarities and difference between DNA and RNA with a comparison table. You can download this article as PDF from the download link provided below.
Difference between DNA and RNA
| Aspect | DNA | RNA |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Deoxyribonucleic Acid | Ribonucleic Acid |
| Sugar Component | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Nitrogenous Bases | Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine | Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine |
| Strand Type | Typically, double-stranded | Typically, single-stranded |
| Function | Long-term storage and transmission of genetic information | Involved in protein synthesis, gene regulation, and catalysis |
| Stability | Highly stable under alkaline conditions | Less stable under alkaline conditions |
| Presence of 2'-Hydroxyl Group | Absent in deoxyribose (increases stability) | Present in ribose (decreases stability) |
| Replication | Self-replicating | Synthesized from DNA template during transcription |
| Enzymes for Synthesis | DNA polymerases | RNA polymerases |
| Location in Eukaryotes | Primarily in the nucleus; small amounts in mitochondria | Found in the nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes |
| Base Pairing Rules | Adenine pairs with Thymine, Cytosine pairs with Guanine | Adenine pairs with Uracil, Cytosine pairs with Guanine |
| Molecular Weight | Generally higher molecular weight due to longer chains | Generally lower molecular weight due to shorter chains |
| Types | One major type, although different forms (e.g., mitochondrial DNA) | Multiple types (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, etc.) |
| Role in Heredity | Direct carrier of hereditary information | Plays a role in the expression of genetic information |
| Sensitivity to UV Light | Less susceptible to UV-induced damage | More susceptible to UV-induced damage |
| Existence of Catalytic Activity | Lacks catalytic activity | Some RNA molecules exhibit catalytic activity (ribozymes) |
Similarities Between DNA and RNA
Nucleic Acid Composition: Both DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides, composed of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases.
Genetic Information Carriers: DNA and RNA both carry genetic information essential for the functioning of organisms, with DNA holding the long-term code and RNA translating this code into proteins.
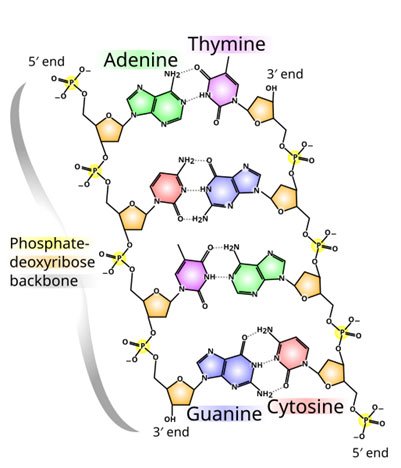
Madprime (talk · contribs), CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Base Pairing: In both DNA and RNA, adenine forms hydrogen bonds with complementary bases, although thymine in DNA is replaced by uracil in RNA.
Phosphodiester Bonds: Both nucleic acids are formed through phosphodiester bonds between the 5′ phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3′ hydroxyl group of the next.
Involvement in Protein Synthesis: DNA stores the genetic instructions, and RNA translates these instructions into proteins during protein synthesis.
Presence of Genetic Mutations: Both DNA and RNA can undergo mutations, leading to changes in genetic information that can be inherited or affect gene expression.
Summary: DNA and RNA are fundamental nucleic acids in biological systems, distinguished by their sugar components, nitrogenous bases, and functional roles. While DNA is the stable genetic repository, RNA serves as the versatile intermediary in gene expression and regulation. Despite their differences, both share essential similarities, such as their nucleotide composition, involvement in genetic information transfer, and role in protein synthesis.
I hope you found this article on Diffeence between DNA and RNA is informative and beneficial. Your feedback and comments would be greatly appreciated. Whether you have suggestions, questions, or thoughts to share, I would be delighted to hear from you. Engaging with your comments helps me continue to produce high-quality content in Biology. Please feel free to leave a comment below. Thank you for your support.
Regards: Admin, EasyBiologyClass
<<< Bac to Molecular Biology Page
Want to read offline? download full PDF: DNA vs RNA Comparison Table
You may also like NOTES in... BOTANY BIOCHEMISTRY MOL. BIOLOGY ZOOLOGY MICROBIOLOGY BIOSTATISTICS ECOLOGY IMMUNOLOGY BIOTECHNOLOGY GENETICS EMBRYOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY EVOLUTION BIOPHYSICS BIOINFORMATICS
