Vascular bundles are the distinct structural organization vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) and the formation of vascular bundles is one of the advanced characteristics of higher plants. In the stem of seed plants, the vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) occupy together as vascular bundles. However, in roots the xylem and phloem are not associated together and not form the vascular bundles. Such an arrangement of vascular tissue in root is called radial arrangement. The present article describes the similarites and difference between collateral and bicollateral vascular bundles.
In the previous post we have discussed the Structure and Classification of Vascular Bundles. Based on the relative position and number of phloem strands in vascular bundles, the conjoint vascular bundles are classified into two groups: (1). Collateral vascular bundles and (2) Bicollateral vascular bundles.
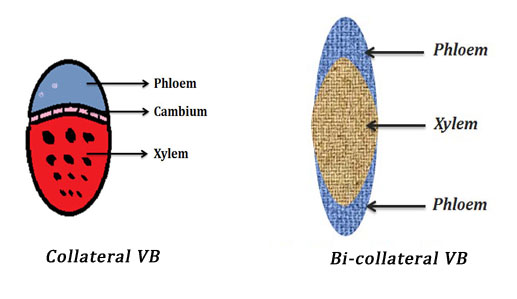
 Collateral vascular bundle
Collateral vascular bundle
A type of conjoint vascular bundle where the xylem occupies inner to a single strand of phloem. Example: dicot stem and monocot stem.
Bicollateral vascular bundles
A type of conjoint vascular bundle where the xylem is situated in the middle of two phloem strands. Example: stem of Cucurbita, Cephalandra (members of Cucurbitaceae Family).
Similarities between Collateral and Bicollateral Vascular Bundles
Ø Both are conjoint vascular bundles (xylem and phloem occupy together as bundle).
Ø Both are present in the stem.
Ø Both contain only one xylem strand.
Ø Xylem is endarch in both the groups.
Difference between Collateral and Bicollateral Vascular Bundle
Sl. No. Collateral Vascular Bundles Bicollateral Vascular Bundles 1 Possess a single patch of phloem. Possess two patches of phloem. 2 Phloem is located external to the xylem (towards the periphery) Phloem occupy on both sides of the centrally placed xylem strand. 3 Contain one strip of cambium between the xylem and phloem Contain two strips of cambium, one between outer phloem and xylem and the other between inner phloem and xylem 4 Collateral vascular bundles can be open (dicot stem) or closed (monocot stem) Bicollateral vascular bundles are always open. 5 Example: Dicot stem (open), monocot stem (closed) Examples: Cucurbita stem, Cephalandra stem

| You may also like... | ||
|---|---|---|
| NOTES | QUESTION BANK | COMPETITIVE EXAMS. |
| PPTs | UNIVERSITY EXAMS | DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. |
| MCQs | PLUS ONE BIOLOGY | NEWS & JOBS |
| MOCK TESTS | PLUS TWO BIOLOGY | PRACTICAL |

 Collateral vascular bundle
Collateral vascular bundle