Dear Students,
Welcome to Genetics MCQ-11 (CSIR NET Genetics Questions) This MCQ set consists of Advanced (Post Graduate Level) Genetics and Molecular Genetics Multiple Choice Questions taken from the previous year question papers of CSIR NET Life Sciences Examination. These questions can be used for the preparation of Competitive examinations in Biology / Life Sciences such as CSIR JRF NET, ICMR JRF, DBT BET JRF, GATE and other University Ph.D Entrance Examinations. After marking your answers, please click ‘SUBMIT‘ button to see your ‘SCORE‘ and ‘CORRECT ANSWERS‘.
You may also like: Genetics Notes | Genetics PPT
Question-1: Following is a hypothetical biochemical pathway responsible for pigmentation of leaves. The pathway is controlled by two independently assorting genes ‘A’ and ‘B’ encoding enzymes as shown below. Mutant alleles ‘a’ and ‘b’ code for non- functional proteins.
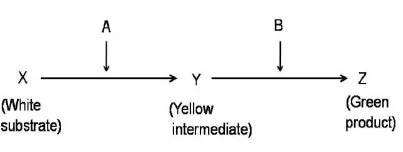
What is the expected progeny after selfing a plant with the genotype AaBb ?
(a). Green (9): White (4): Yellow (3)
(b). Green (9): Yellow (4): White (3)
(c). Green (9): Yellow (6): White (1)
(d). Green (9): White (7)
Ans. (a).
Question-2: Mutation in gene ‘X’ leads to lethality in a haploid organism. Which one of the following is best suited to analyse the function of gene ‘X’?
(a). Pleiotropic mutants
(b). Temperature-sensitive mutants
(c). Recessive mutants
(d). Mutants with low penetrance
Ans. (b)
Question-3: The following pedigree chart shows inheritance of a given trait
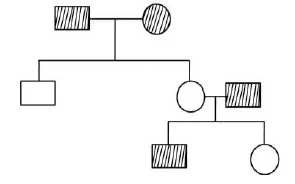
The trait can be called:
(a). Autosomal dominant
(b). Autosomal recessive
(c). X-linked dominant
(d). Sex limited
Ans. (a)
Question-4: Of the following, which one of the individuals will NOT necessarily carry the allele responsible for the mentioned trait?
(a). A woman in a family where an autosomal dominant trait is segregating and her mother and son are affected.
(b). A daughter of a man who is affected by an X-linked dominant trait
(c). A father of a child who is affected with an autosomal recessive trait
(d). A father of a boy affected with X-linked recessive trait
Ans. (d)
Question-5: Poplar is a dioecious plant. A wild plant with 3 genes AABBCC was crossed with a triple recessive mutant aabbcc. The F1 male hybrid (AaBbCc) was then back crossed with the triple mutant and the phenotypes recorded are as follows:
AaBbCc – 300
aaBbCc – 100
aaBbcc – 16
AabbCc – 14
AaBbcc – 65
aabbCc – 75
aabbcc – 310
Aabbcc – 120
The distance in map unit (mu) between A to B and B to C is:
(a). 25 and 17 mu, respectively
(b). 33 and 14 mu, respectively
(c). 25 and 14 mu, respectively
(d) . 33 and 17 mu, respectively
Ans. (a)
Question-6: Fruit colour of wild Solanum nigrum is controlled by two alleles of a gene (A and a). The frequency of A, p=0.8 and a, q=0.2. In a neighbouring field a tetraploid genotype of S. nigrum was found. After critical examination five distinct genotypes were found; which are AAAA, AAAa, AAaa, Aaaa and aaaa. Following Hardy Weinberg principle and assuming the same allele frequency as that of diploid population, the numbers of phenotypes calculated within a population of 1000 plants are close to one of the following:
AAAA : AAAa : AAaa : Aaaa : aaaa
(a). 409 : 409 : 154 : 26 : 2
(b). 420 : 420 : 140 : 18 : 2
(c). 409 : 409 : 144 : 36 : 2
(d). 409 : 420 : 144 : 25 : 2
Ans. (a)
Question-7: A three point test cross was carried out in Drosophila melanogaster involving three adjacent genes X, Y and Z, arranged in the same order. The distance between X to Y is 32.5 map unit (mu) and that between X to Y is 20.5 map. The coefficient of coincidence = 0.886. What is the percentage of double recombinants in the progeny obtained from the testcross?
(a). ~6%
(b). ~8%
(c). ~12%
(d). ~16%
Ans. (a)
Question-8: Two interacting genes (independently assorting) were involved in the same pathway. Absence of either genes function leads to absence of the end product of the pathway. A dihybrid cross involving the two genes is carried out. What fraction of the F2 progeny will show the presence of the end product?
(a). ¼
(b). 3/4
(c). 9/16
(d) . 15/16
Ans. (c)
Question-9: A male mouse cell line has a large translocation from X chromosome into chromosome 1. When a GFP containing transgene is inserted in this chromosome 1 with translocation, it is often silenced. However when inserted in the other homologue of chromosome 1 that does not contain the translocation, it is almost always expressed. Which of the following phenomenon best describes this effect?
(a). Genome imprinting
(b). Gene balance
(c). Sex-specific expression
(d). Dosage compensation
Ans. (d)
Question-10: Consider an autosomal locus with two alleles A1 and A2 at frequencies of 0.6 and 0.4 respectively. Each generation, A1 mutates to A2 at a rate of μ = 1 X 10-5 while A2 mutates to A1 at a rate of μ = 2 X 10-5. Assume that the population is infinitely large and no other evolutionary force is acting. The equilibrium frequency of allele A1 is:
(a). 1.0.
(b). 0.5.
(c). 0.67.
(d). 0.33.
Ans. (c)
You may also like... NOTES QUESTION BANK COMPETITIVE EXAMS. PPTs UNIVERSITY EXAMS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. MCQs PLUS ONE BIOLOGY NEWS & JOBS MOCK TESTS PLUS TWO BIOLOGY PRACTICAL