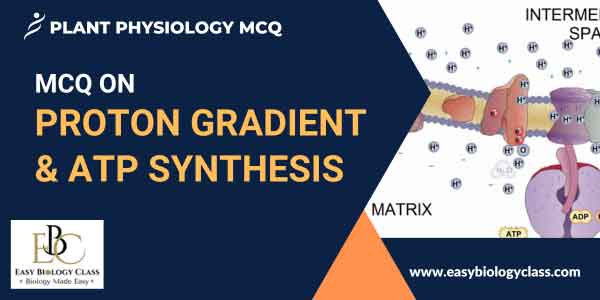
A proton gradient is a difference in proton concentration across a membrane, created by the electron transport chain. ATP synthesis occurs when protons flow back across the membrane through ATP synthase, using the energy from this gradient to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate into ATP. This article is on Proton Gradient and ATP Synthesis explained in an MCQ format.
<<< Back to Plant Physiology MCQ Page
You may also like... NOTES QUESTION BANK COMPETITIVE EXAMS. PPTs UNIVERSITY EXAMS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. MCQs PLUS ONE BIOLOGY NEWS & JOBS MOCK TESTS PLUS TWO BIOLOGY PRACTICAL