Maximum Parsimony Method Explained for Students
Introduction
The Maximum Parsimony Method is a widely used technique in phylogenetics. It helps scientists and students study evolutionary relationships among plants. This method chooses the tree that requires the fewest evolutionary changes. Therefore, it follows the principle of simplicity, making it easy to understand and apply. In botany, this method is applied to species like mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and flowering plants. Its simplicity and logical framework make it ideal for student learning and basic evolutionary studies. You can easily download this note as a PDF using the link provided just below the post for quick access and offline reading.
Taxonomy Notes | Evolution Notes | Taxonomy PPTs | Evolution PPTs
Definition
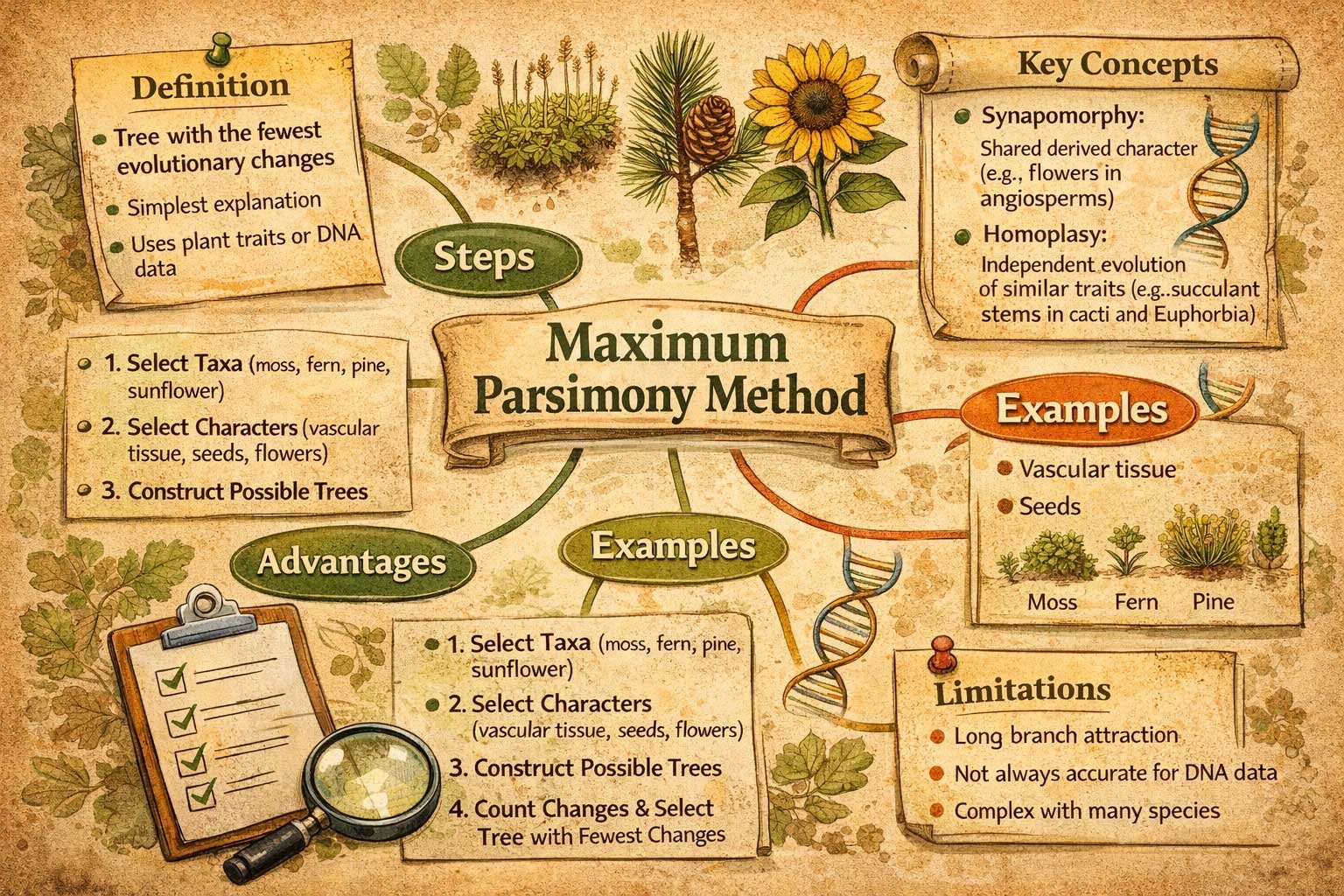
Maximum Parsimony Method is a phylogenetic approach that selects the evolutionary tree with the fewest character changes. It assumes that the simplest explanation is usually correct. This method helps students construct evolutionary trees using observable plant traits or molecular data.
The Maximum Parsimony Method is based on a simple principle: the best evolutionary tree is the one with the smallest number of changes in traits.
This method is guided by Occam’s Razor, which suggests that the simplest explanation is preferred. In phylogenetics, “simplest” means minimizing the total number of evolutionary steps.
For example, if Tree A requires three changes and Tree B requires five, Tree A is considered more accurate. The method helps visualize evolutionary pathways clearly and logically.
Characters Used in Plant Phylogenetic Analysis
Characters are the features used to compare plants in Maximum Parsimony analysis. These traits are divided into three main types:
Morphological Characters
Visible plant traits include:
- Leaf shape
- Presence of vascular tissue
- Seed type (naked or enclosed)
- Flower structure
Example coding:
- Seed type: 0 = Naked (gymnosperm), 1 = Enclosed (angiosperm)
- Flower presence: 0 = Absent, 1 = Present
Anatomical Characters
Internal structures are also considered:
- Stomatal type
- Wood structure
- Arrangement of vascular bundles
Molecular Characters
DNA sequences provide molecular data:
- rbcL gene
- Chloroplast DNA regions
Each character has different states, which are coded numerically for analysis.
Steps in the Maximum Parsimony Method
The Maximum Parsimony Method follows a stepwise approach:
Step 1: Select Taxa
Choose the plant species to analyze.
Example taxa:
- Moss
- Fern
- Pine
- Sunflower
You may also like NOTES in... BOTANY BIOCHEMISTRY MOL. BIOLOGY ZOOLOGY MICROBIOLOGY BIOSTATISTICS ECOLOGY IMMUNOLOGY BIOTECHNOLOGY GENETICS EMBRYOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY EVOLUTION BIOPHYSICS BIOINFORMATICS
Step 2: Select Characters
Choose traits that vary among these species:
- Presence of vascular tissue
- Presence of seeds
- Presence of flowers
Step 3: Construct Possible Trees
Generate all possible evolutionary trees connecting the selected species. Each tree represents a different hypothesis about evolutionary relationships.
Step 4: Count Evolutionary Changes
For each tree:
- Count how many changes occur in all characters.
- Compare totals across trees.
- Select the tree with the fewest changes.
This tree is the most parsimonious tree.
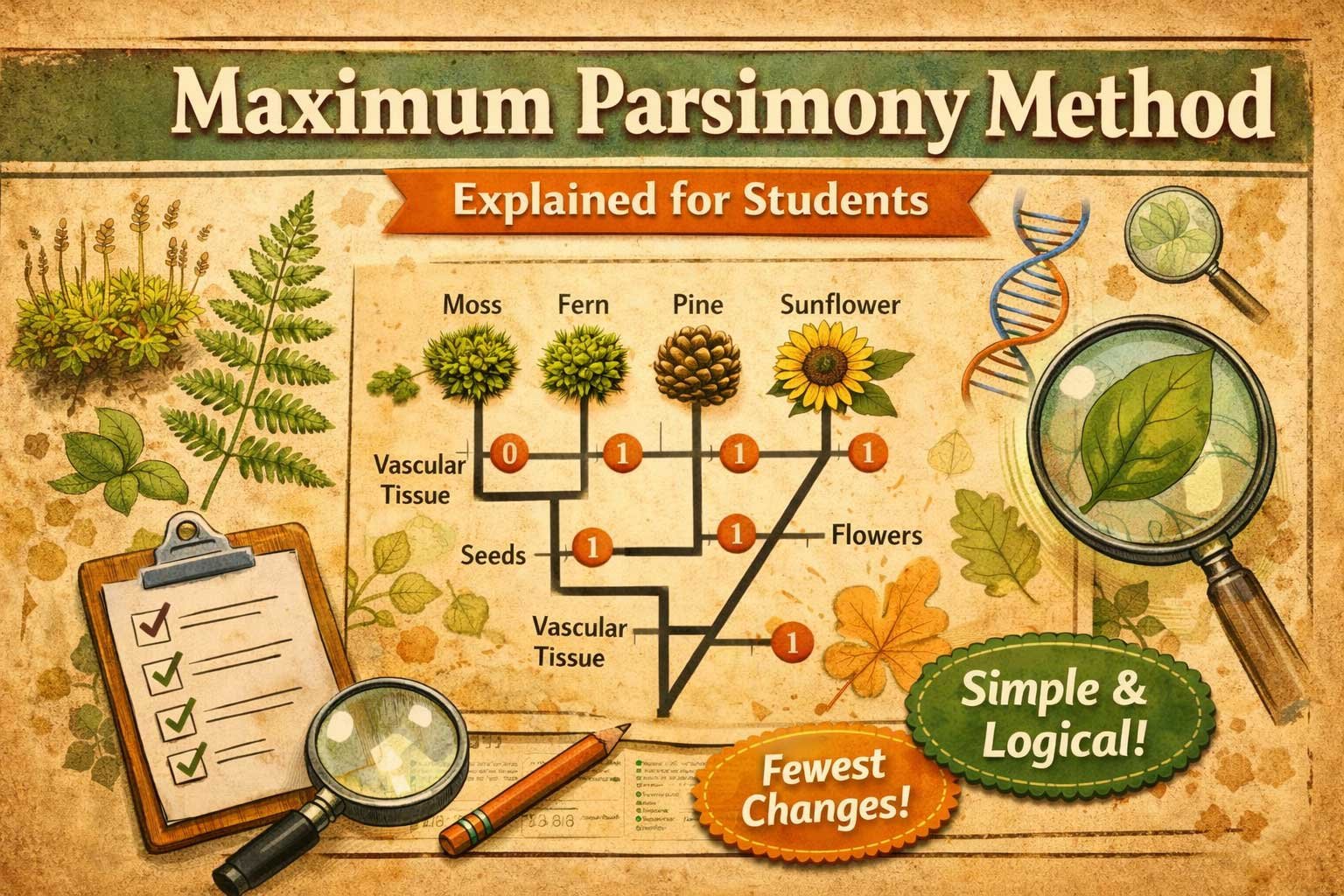
Example of Maximum Parsimony in Plants
Compare four plants:
- Moss
- Fern
- Pine
- Sunflower
Examine three characters: vascular tissue, seeds, and flowers.
If a tree shows:
- Vascular tissue evolved once
- Seeds evolved once
- Flowers evolved once
Total changes = 3.
Another tree may require 4 or 5 changes. The tree with 3 changes is selected as the most parsimonious.
This example demonstrates how the method identifies the simplest evolutionary path.
Key Concepts in Maximum Parsimony Method
Synapomorphy
A synapomorphy is a shared derived character.
Example: Flowers are a synapomorphy of angiosperms.
Homoplasy
Homoplasy occurs when similar traits evolve independently in unrelated groups.
Example: Succulent stems evolved in both cacti and Euphorbia. Homoplasy increases character changes and can complicate tree selection.
Most Parsimonious Tree
The most parsimonious tree requires the fewest total evolutionary steps. Sometimes, multiple equally parsimonious trees exist.
Applications in Plant Evolution
Maximum Parsimony is widely applied in botany:
- Studying the evolution of angiosperms
- Determining monocot and dicot origins
- Analyzing gymnosperm relationships
- Investigating floral structure evolution
It is especially useful for fossil plants where molecular data may not be available.
Advantages of the Maximum Parsimony Method
- Simple and easy to understand
- Does not require complex statistical models
- Effective for morphological and fossil data
- Suitable for small datasets and teaching purposes
Limitations of the Maximum Parsimony Method
Long Branch Attraction
Rapidly evolving species may appear closely related, reducing accuracy.
Large DNA Datasets
For extensive molecular datasets, methods like Maximum Likelihood or Bayesian Inference may provide better results.
Computational Complexity
Many species lead to a huge number of possible trees, making calculations more complex.
Comparison with Other Phylogenetic Methods
| Method | Principle |
|---|---|
| Maximum Parsimony | Fewest evolutionary changes |
| Maximum Likelihood | Tree with highest probability under a model |
| Bayesian Inference | Probability-based with prior information |
Maximum Parsimony does not use statistical models. It relies solely on minimizing character changes.
MCQs for Practice (Complete)
- The Maximum Parsimony Method selects a phylogenetic tree that:
- A. Has the longest evolutionary pathway
- B. Has the highest mutation rate
- C. Requires the fewest evolutionary changes
- D. Has the greatest number of taxa
Answer: C – It selects the tree minimizing total character changes.
- In plant phylogenetic analysis, which is a morphological character?
- A. rbcL gene sequence
- B. Chloroplast DNA region
- C. Flower presence or absence
- D. Nucleotide substitution rate
Answer: C – Morphological characters are visible traits.
- Evolution of seeds in gymnosperms and angiosperms is:
- A. Primitive character in moss
- B. Synapomorphy for seed plants
- C. Homoplasy in angiosperms
- D. Molecular marker
Answer: B – Shared derived character of seed plants.
- Independent evolution of succulent stems in unrelated plants represents:
- A. Synapomorphy
- B. Shared ancestral character
- C. Homoplasy due to convergent evolution
- D. Parsimony
Answer: C – Trait evolved independently, not shared ancestry.
- Which situation reduces Maximum Parsimony accuracy?
- A. Use of morphological data
- B. Small number of taxa
- C. Long branch attraction
- D. Fossil analysis
Answer: C – Rapidly evolving lineages may cluster falsely.
- Tree A requires 8 changes, Tree B 6, Tree C 7. Maximum Parsimony selects:
- A. Tree A
- B. Tree B
- C. Tree C
- D. All equally preferred
Answer: B – Tree B has the fewest evolutionary steps.
Conclusion
The Maximum Parsimony Method is a foundational technique in phylogenetics. It selects the evolutionary tree with the smallest number of character changes. This method is simple, logical, and student-friendly. It remains important for morphological studies, fossil analysis, and teaching plant evolutionary relationships. By understanding this method, students build a strong foundation in botany and evolutionary systematics.
Taxonomy Notes | Evolution Notes | Taxonomy PPTs | Evolution PPTs
Study Offline!! Download this Note as a PDF
You may also like... NOTES QUESTION BANK COMPETITIVE EXAMS. PPTs UNIVERSITY EXAMS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. MCQs PLUS ONE BIOLOGY NEWS & JOBS MOCK TESTS PLUS TWO BIOLOGY PRACTICAL
🌿 Dear Readers,
I hope you found this article helpful and easy to understand. If you have any questions, suggestions, or thoughts, I would truly love to hear from you.
Please share your feedback in the comments below. Your participation helps make EasyBiologyClass a better learning space for everyone.
Best regards,
EasyBiologyClass
