Mitosis and meiosis are fundamental processes of cell division that facilitate the growth, development, and reproduction of organisms. Mitosis is a process of nuclear division that results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells from a single parent cell, primarily for growth and tissue repair in multicellular organisms. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing four genetically distinct gametes or spores, essential for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Here we discuss the similarities and difference between mitosis and meiosis with a comparison table. You can download the notes as PDF from the download link provided below.
Distinguish between Mitosis and Meiosis
Aspect Mitosis Meiosis Purpose Growth, repair, and asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction - production of gametes Number of Divisions One division Two sequential divisions (Meiosis I and Meiosis II) Phases Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase Meiosis-I: Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase
Meiosis-II: Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase IINumber of Daughter Cells Two daughter cells are formed Four daughter cells are formed Genetic Composition of Daughter Cells Genetically identical to the parent cell Genetically diverse, each with half the chromosome number Chromosome Number Maintains the same chromosome number as the parent cell (diploid) Reduces the chromosome number by half (haploid) Occurrence Occurs in somatic cells Occurs in germ cells (gametes) Homologous Chromosome Pairing No pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs Homologous chromosomes pair and undergo synapsis Crossing Over No crossing over occurs Crossing over occurs during Prophase I, leading to genetic recombination Centromere Division Centromeres divide during anaphase Centromeres do not divide during Meiosis I but do during Meiosis II Synapsis of Homologs Does not occur Occurs during Prophase I
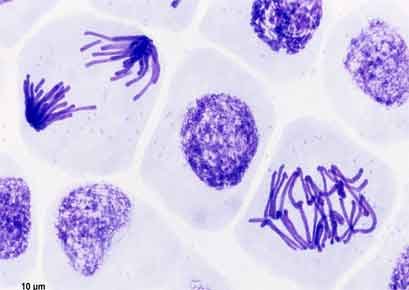
Mitotic Stages in Meristematic Cells
Similarities Between Mitosis and Meiosis
Ø Basic Process of Division: Both mitosis and meiosis involve the division of a parent cell into daughter cells through stages that include prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Ø Requirement of DNA Replication: Both processes are preceded by a single round of DNA replication during the S phase of the cell cycle.
Ø Role of Spindle Apparatus: In both processes, the spindle apparatus is crucial for the separation of chromosomes and their movement to opposite poles of the cell.
Ø Involvement of Cytokinesis: Both processes conclude with cytokinesis, where the cytoplasm divides, resulting in separate daughter cells.
Ø Phases of Division: Both mitosis and meiosis include similar phases, albeit in meiosis the sequence is repeated with modifications during meiosis I and II.
Summary
Mitosis and meiosis are critical cellular processes with distinct roles in growth, development, and reproduction. Mitosis ensures the maintenance of genetic consistency across somatic cells, facilitating organismal growth and repair. In contrast, meiosis introduces genetic diversity through the production of haploid gametes, essential for sexual reproduction and evolution.
I hope you found this article on Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis is informative and beneficial. Your feedback and comments would be greatly appreciated. Whether you have suggestions, questions, or thoughts to share, I would be delighted to hear from you. Engaging with your comments helps me continue to produce high-quality content in Biology. Please feel free to leave a comment below. Thank you for your support.
Regards: Admin, EasyBiologyClass
Want to read offline? Download full PDF: Difference between Mitosis and Meiosis
<<< Back to Cell Biology Notes
You may also like NOTES in... BOTANY BIOCHEMISTRY MOL. BIOLOGY ZOOLOGY MICROBIOLOGY BIOSTATISTICS ECOLOGY IMMUNOLOGY BIOTECHNOLOGY GENETICS EMBRYOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY EVOLUTION BIOPHYSICS BIOINFORMATICS
