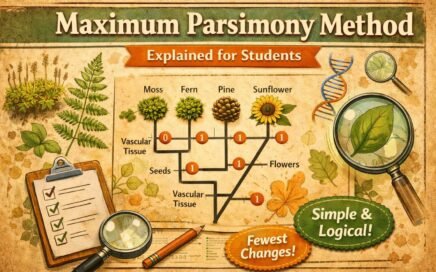
Type Method in Taxonomy (Nomenclatural Type)
Type Method Taxonomy (Nomenclatural Type) Type Method Taxonomy is a fundamental principle of biological classification. It ensures that each taxonomic name is permanently linked to a specific representative. Therefore, it maintains stability and clarity in naming organisms. In botanical nomenclature, this method plays a central role in identifying families, genera, […]