How to Calculate pH and pKa of a Buffer using Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation?
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is a numerical expression which relates the pH, pKa and Buffer Action of a buffer. A buffer is a solution which can resist the change in pH. Chemically, a buffer is a solution of equimolar concentration of a weak acid (such as acetic acid – CH3COOH) and its conjugate base (such as acetate ion – CH3COO¯). In the previous post, we have discussed the Titration Curve of a weak acid and the Derivation of Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation.
The characteristic shape of the titration curve of a weak acid is also described by the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. In this chapter we will discuss the methods to calculate the pH or pKa of a buffer using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation using sample problems.
Learn more: Titration Curve of a Weak Acid (Acetic Acid)
Lean more: How to Derive Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation?
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation is given as:

Where,
pH – the negative logarithm of H⁺ ion concentration in the medium.
pKa – the negative logarithm of Ka of the acid (Ka is the dissociation constant)
Proton acceptor – the ionized or deprotonated acid (example – CH3COO¯).
Proton donor – intact (non-ionized) weak acid (example – CH3COOH).
| You may also like NOTES in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| BOTANY | BIOCHEMISTRY | MOL. BIOLOGY |
| ZOOLOGY | MICROBIOLOGY | BIOSTATISTICS |
| ECOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | BIOTECHNOLOGY |
| GENETICS | EMBRYOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY |
| EVOLUTION | BIOPHYSICS | BIOINFORMATICS |
Let’s see some sample problems and solutions.
Problem-1: A mixture of 0.20M acetic acid and 0.30M sodium acetate is given. Calculate the pH of the medium if the pKa of the acetic acid is 4.76.
Solution:
This is a straight question and you can directly apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation. All the required components to calculate the pH are given in the question itself.
Following components are given in the question:
The concentration of acetic acid (proton donor) = 0.20M
The concentration of acetate ion (proton acceptor) = 0.30M
The pKa of acetic acid = 4.76
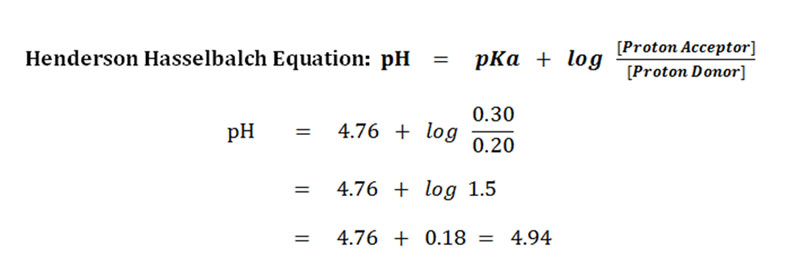
Answer: The pH of the given solution is 4.94
Problem-2: The pH of the given solution of lactic acid and lactate is 4.30. Calculate the pKa of lactic acid, when the concentration of lactic acid and lactate are 0.020M and 0.073M respectively.
Solution:
Following components are given in the question:
pH of the medium = 4.30
Concentration of lactate ion (proton acceptor) = 0.073M
Concentration of lactic acid (proton donor) = 0.020M

We need to calculate the pKa of lactic acid. So, take out the pKa to the left side and the equation now becomes:


Answer: The pKa of the given solution is 3.74
| You may also like... | ||
|---|---|---|
| NOTES | QUESTION BANK | COMPETITIVE EXAMS. |
| PPTs | UNIVERSITY EXAMS | DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. |
| MCQs | PLUS ONE BIOLOGY | NEWS & JOBS |
| MOCK TESTS | PLUS TWO BIOLOGY | PRACTICAL |
Problem-3: What is the ratio of the concentration of acetic acid and acetate ions required to prepare a buffer with pH 5.20. The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76.
Solution:
You cannot direct apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation here because it is an indirect question. First you need to rearrange the equation accordingly.
Following components are given in the question:
pH of the buffer = 5.20
pKa of acetic acid = 4.76


Answer: The ratio of acetate to acetic acid required to get a pH of 5.20 is 2.75
You might also like…
@. How to Derive Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
@. Titration Curve of Weak Acid

Its’s extremely adorable. Thank to you for sharing and elevating the knowledge. It’s worthy to join and invite my entire pals.
Best Regard
Nurul Hasan
Thank you