If you’re studying biology, you’ve likely come across the term “Double Fertilization” in your textbooks. But what exactly is it, and why is it so important in the world of plants? In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating process of double fertilization in flowering plants, breaking it down step-by-step to ensure you have a clear and comprehensive understanding of this crucial biological phenomenon.
What is Double Fertilization?
Double fertilization is a unique and intricate process that occurs in flowering plants (angiosperms). This process involves the fusion of a female gametophyte or megagametophyte, also called the embryonic sac, with two male gametes (sperm). This process results in the formation of both zygote and endosperm, essential for the development of seeds and ultimately the next generation of plants.
The Process of Double Fertilization
Let’s break down the steps of double fertilization:
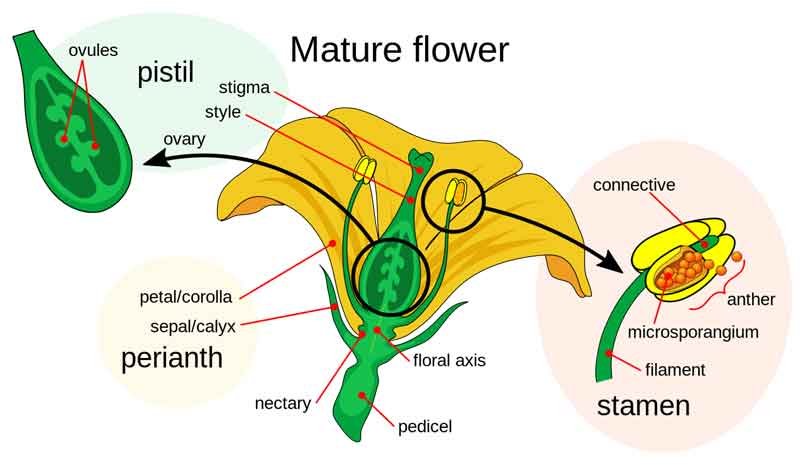
- Pollination: The journey begins when pollen grains from the male anther land on the female stigma. This can happen through various means such as wind, water, or pollinators like bees.
- Pollen Tube Formation: Once a pollen grain lands on a compatible stigma, it germinates, forming a pollen tube that grows down through the style toward the ovary.
- Sperm Cell Travel: Inside the pollen tube are two sperm cells. These cells travel down the tube, heading toward the ovule, which contains the female gametophyte (embryo sac).
- Entry into the Ovule: The pollen tube penetrates the ovule through an opening called the micropyle.
Double Fertilization: Here’s where the magic happens:
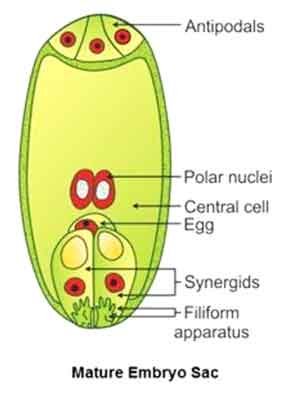
- The mature embryonic sac of an unfertilized ovule consists of 7 cells and 8 nuclei.
- These cells and nuclei are organized from top to bottom as:
- 3 antipodal cells
- 1 central (binucleate) cell
- 2 synergids
- 1 egg cell
- One sperm fertilizes the egg cell.
- The other sperm fuses with the two polar nuclei of the large central cell of the megagametophyte.
- The haploid sperm and egg fuse to form a diploid zygote, a process known as syngamy.
- The other sperm and the diploid central cell fuse to create a triploid primary endosperm cell in a process called triple fusion.
- The large cell of the gametophyte then develops into the endosperm, a nutrient-rich tissue that nourishes the developing embryo.
- The ovary, which surrounds the ovules, develops into the fruit, protecting the seeds and aiding in their dispersal.
Two fertilization events, hence called Double Fertilization
First Fertilization: One sperm cell fuse with the egg cell, forming a diploid zygote (2n). This zygote will eventually develop into the embryo.
Second Fertilization: The second sperm cell fuses with two polar nuclei in the central cell of the embryo sac, forming a triploid cell (3n). This triploid cell develops into the endosperm, a tissue that provides nourishment to the developing embryo.
Why double fertilization is called as Triple Fusion?
The process of double fertilization (exactly in the second fertilization) involves the fusion of three nuclei, two polar nuclei and one male gamete to form the triploid (3n) endosperm mother cell. Due to involvement of three nuclei, the double fertilization is also called as triple fusion.
Importance of Double Fertilization
Efficient Use of Resources: By coordinating the development of the embryo and its food supply, plants ensure that energy is not wasted. The endosperm only develops if fertilization is successful, which is a resource-efficient strategy.
Seed Development: The formation of both the embryo and endosperm is essential for the development of viable seeds, which are critical for the propagation of flowering plants.
Genetic Variation: The process promotes genetic diversity by combining genetic material from two parent plants, which can lead to variations in offspring that may be better adapted to their environments.
Conclusion
Double fertilization is a remarkable process that highlights the complexity and efficiency of plant reproductive strategies. By understanding the steps and significance of double fertilization, undergraduate biology students can appreciate how flowering plants successfully reproduce and ensure the survival of their species.
<<< Back to Plant Embryology Notes
| You may also like NOTES in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| BOTANY | BIOCHEMISTRY | MOL. BIOLOGY |
| ZOOLOGY | MICROBIOLOGY | BIOSTATISTICS |
| ECOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | BIOTECHNOLOGY |
| GENETICS | EMBRYOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY |
| EVOLUTION | BIOPHYSICS | BIOINFORMATICS |