MCQ on C4 Cycle (Hatch and Slack pathway)
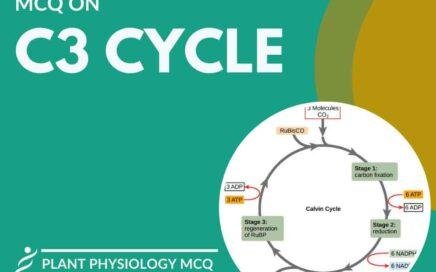
The C4 cycle (Hatch and Slack Pathway) is a photosynthetic process in some plants where CO₂ is initially fixed into a four-carbon compound. This adaptation minimizes photorespiration and enhances efficiency by concentrating CO₂ around RuBisCO, enabling better performance under high light intensity, high temperatures, and low CO₂ conditions. This is […]