Botanical Nomenclature: Complete Student Guide
Introduction
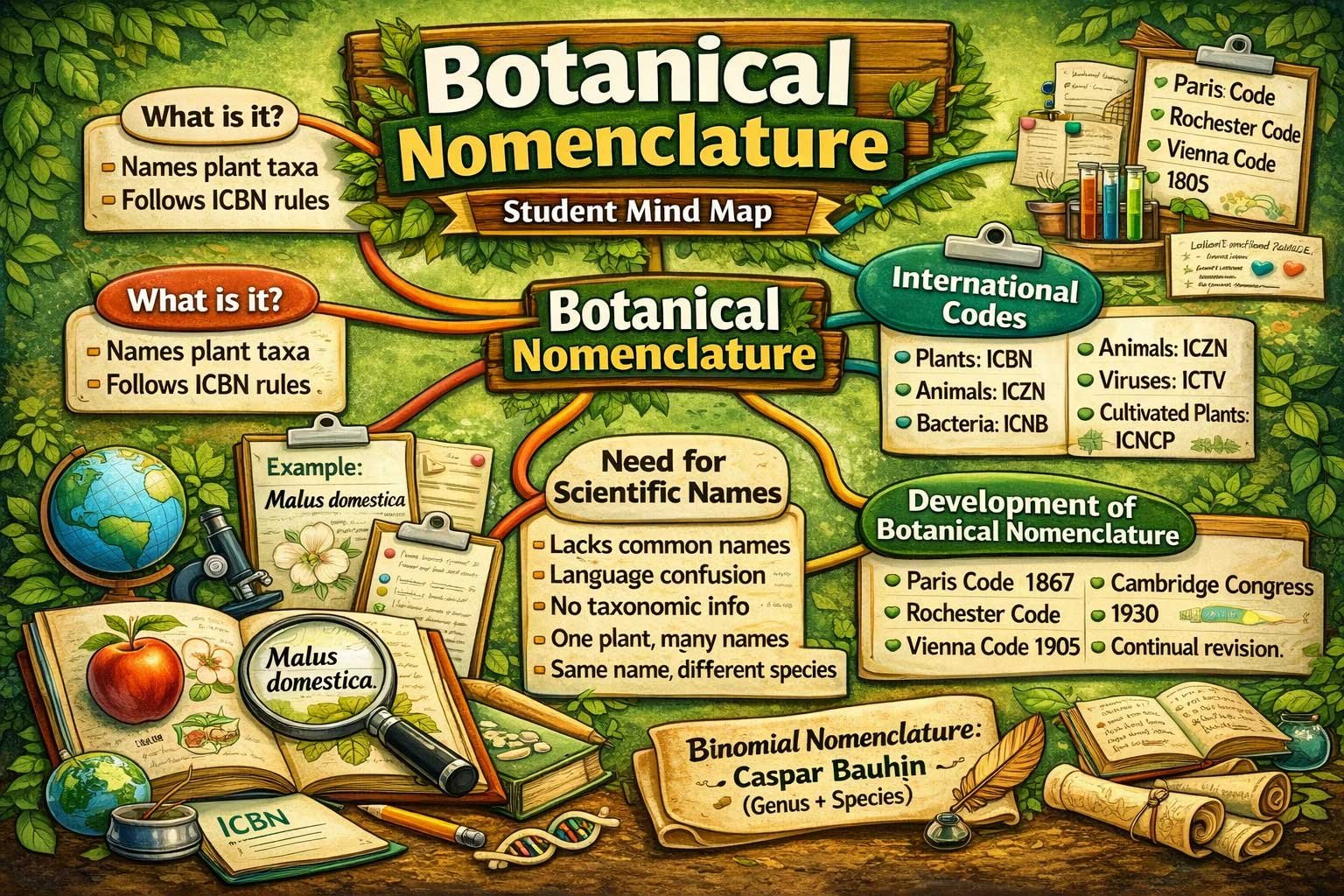
Botanical nomenclature is the system used to assign correct scientific names to plants. It ensures that each plant species has one accepted name worldwide. Therefore, scientists avoid confusion caused by common names. This system follows international rules and codes. In addition, it connects plant identification with proper naming. As a result, students and researchers communicate clearly and accurately. You can easily download this note as a PDF using the link provided just below the post for quick access and offline reading.
Plant Taxonomy Notes | Plant Taxonomy PPTs | Plant Taxonomy MCQs
📘 Definition
Botanical nomenclature is the scientific system of naming plants according to internationally accepted rules. It ensures that every plant taxon has one correct Latin name. Thus, it avoids confusion created by local or common names and promotes universal scientific communication.
What is Botanical Nomenclature?
Botanical nomenclature deals with assigning correct names to plant taxa. It works closely with plant identification. When a botanist identifies a plant specimen, the correct scientific name must also be applied.
For example, apple is known by many names. However, its correct scientific name is Malus domestica. Only this name combines identification with proper nomenclature.
Today, botanical nomenclature follows rules set by the International Association of Plant Taxonomy. These rules are published in the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature. The code is revised after each International Botanical Congress.

International Codes of Nomenclature
Different groups of organisms follow different naming codes. However, each code ensures that no two taxa under the same code share the same scientific name.
- Plants follow the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature.
- Animals follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature.
- Bacteria follow the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria.
- Viruses follow the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses guidelines.
- Cultivated plants follow the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants.
Interestingly, the same generic name may exist in different codes. For example, Cecropia refers to both moths and tropical trees under separate codes.
In recent years, scientists proposed unified systems such as BioCode and PhyloCode. However, global acceptance is still under discussion.
You may also like NOTES in... BOTANY BIOCHEMISTRY MOL. BIOLOGY ZOOLOGY MICROBIOLOGY BIOSTATISTICS ECOLOGY IMMUNOLOGY BIOTECHNOLOGY GENETICS EMBRYOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY EVOLUTION BIOPHYSICS BIOINFORMATICS
Need for Scientific Names in Botanical Nomenclature
Scientific names are preferred over common names for several reasons.
1. Lack of Universal Common Names
Not all species have vernacular names. Therefore, scientific names ensure every species has a recognized identity.
2. Language Limitation
Common names are local. They differ between regions and languages. However, scientific names are universal.
3. No Taxonomic Information
Common names do not show relationships. For example:
- Rosa belongs to Rosaceae.
- Ipomoea belongs to Convolvulaceae.
- Primula belongs to Primulaceae.
Thus, scientific names indicate genus and family relationships clearly.
4. Multiple Common Names for One Species
A single plant may have many local names. This creates confusion in communication.
5. Same Common Name for Different Species
Sometimes, unrelated plants share one common name. Therefore, scientific names prevent misunderstanding.
Why Latin is Used in Botanical Nomenclature
Scientific names are treated as Latin, regardless of their origin. Moreover, Latin was traditionally used by scholars in Europe.
Latin offers several advantages:
- It is a dead language. Therefore, meanings do not change over time.
- It provides precision and clarity.
- Gender forms are grammatically clear.
- It uses the Roman alphabet, which fits global publications.
Because of these benefits, Latin remains the standard language of botanical nomenclature.
Development of Botanical Nomenclature
Early Naming System
Earlier, plant names were long descriptive phrases called polynomials. These names were difficult to remember and use.
For example, a willow species once had a long descriptive name instead of a simple two-word name.

Introduction of Binomial Nomenclature
The concept of binomial naming was introduced by Caspar Bauhin. He suggested that each species should have two names:
- Genus name
- Specific epithet
For example, onion is named Allium cepa.
However, it was Carl Linnaeus who firmly established this system in his book Species Plantarum (1753). Therefore, 1753 is considered the starting point of modern plant nomenclature.
Evolution of the Botanical Code
Several botanical congresses helped develop uniform rules.
Paris Code (1867)
Adopted during the first International Botanical Congress in Paris. It established the rule of priority.
Rochester Code (1892)
American botanists proposed this code. It introduced the concept of type specimens.
Vienna Code (1905)
This code confirmed 1753 as the starting point. It rejected tautonyms and required Latin descriptions.
Cambridge Congress (1930)
This congress unified previous differences. It accepted:
- Type method
- Rejection of tautonyms
- Mandatory Latin diagnosis
- Conserved generic names

Since then, the Code has been revised at every International Botanical Congress.
For example:
- 15th Congress – Tokyo (1993)
- 16th Congress – St. Louis (1999)
- 17th Congress – Vienna (2005)
- 18th Congress – Melbourne (2011)
Each revision improves clarity and global consistency in botanical nomenclature.

Importance of Botanical Nomenclature in Modern Botany
Botanical nomenclature plays a central role in plant science.
- It ensures global communication.
- It supports research and biodiversity studies.
- It maintains uniformity in databases.
- It reduces ambiguity in scientific publications.
In addition, modern digital plant databases depend heavily on standardized naming systems.
If you are studying plant taxonomy, you may also read our guide on Plant Taxonomy Principles (internal link suggestion).

Conclusion
Botanical nomenclature provides a universal system for naming plants. It follows internationally accepted codes and ensures clarity in scientific communication. Moreover, it prevents confusion caused by common names. Therefore, understanding botanical nomenclature is essential for every student of botany and plant taxonomy.
🔷 Competitive MCQs on Botanical Nomenclature
MCQ 1: Which organization publishes the rules governing botanical nomenclature?
A. International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
B. International Association of Plant Taxonomy
C. World Health Organization
D. Food and Agriculture Organization
Answer: B
MCQ 2: The starting point for modern plant nomenclature is based on the publication of:
A. Critica Botanica (1737)
B. Philosophia Botanica (1751)
C. Species Plantarum (1753)
D. Nomenclator Botanicus (1821)
Answer: C
MCQ 3: Which of the following correctly explains why Latin is used in botanical nomenclature?
A. It is widely spoken globally.
B. It changes frequently and adapts easily.
C. It is a dead language with stable meanings.
D. It originated in modern botanical research.
Answer: C
MCQ 4: The concept of binomial nomenclature was first introduced by:
A. Alphonse de Candolle
B. Carl Linnaeus
C. Caspar Bauhin
D. George Bentham
Answer: C
MCQ 5: Which code governs the naming of cultivated plants?
A. International Code of Zoological Nomenclature
B. International Code of Botanical Nomenclature
C. International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria
D. International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants
Answer: D
🔷 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Botanical Nomenclature
FAQ 1: What is botanical nomenclature?
Botanical nomenclature is the scientific system of naming plants according to internationally accepted rules. It ensures that every plant species has one correct and universally recognized name.
FAQ 2: Why are scientific names preferred over common names?
Scientific names are universal and precise. In contrast, common names vary by region and language. Moreover, one species may have many common names, or one common name may refer to different species.
FAQ 3: Why is 1753 important in plant nomenclature?
The year 1753 marks the publication of Species Plantarum by Carl Linnaeus. It is considered the official starting point of modern botanical nomenclature.
FAQ 4: What is binomial nomenclature?
Binomial nomenclature is a system in which each species has a two-part name: the genus name and the specific epithet. For example, Allium cepa.
FAQ 5: Can the same scientific name exist in different biological codes?
Yes. The same generic name may appear under different codes. For example, a name used in botany may also be used in zoology because each code functions independently.
<<< Back to Plant Taxonomy Archives
You may also like... NOTES QUESTION BANK COMPETITIVE EXAMS. PPTs UNIVERSITY EXAMS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. MCQs PLUS ONE BIOLOGY NEWS & JOBS MOCK TESTS PLUS TWO BIOLOGY PRACTICAL
🌿 Dear Readers,
I hope you found this article helpful and easy to understand. If you have any questions, suggestions, or thoughts, I would truly love to hear from you.
Please share your feedback in the comments below. Your participation helps make EasyBiologyClass a better learning space for everyone.
Best regards,
EasyBiologyClass
